Introduction
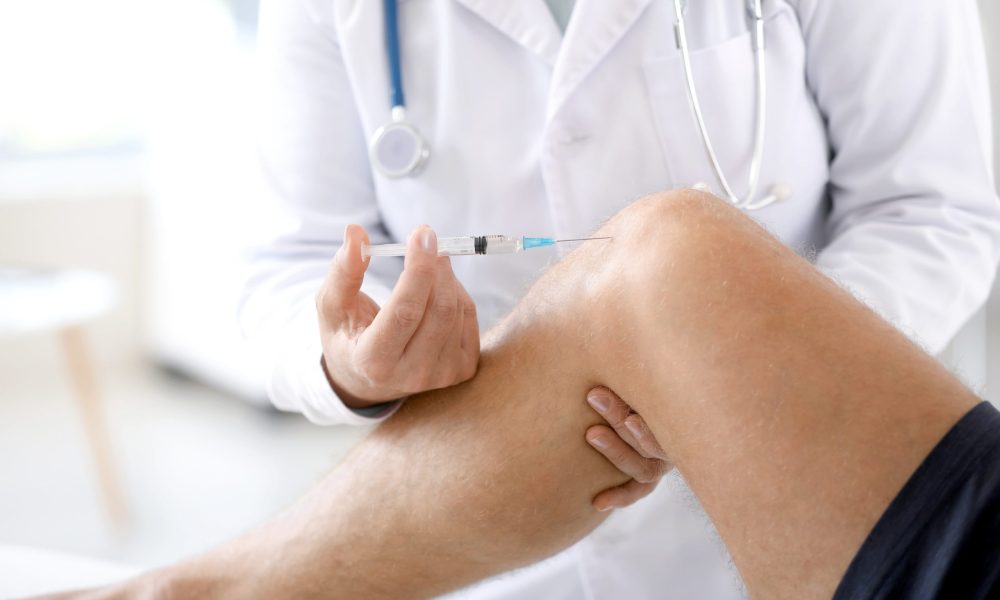
Joint injections are a commonly used medical procedure for managing joint pain and inflammation. They involve directly injecting medication into the affected joint to relieve and improve joint function. Joint injections are used in various conditions that affect the joints, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, bursitis, tendinitis, and gout, among others. These injections can be performed using different medications, such as corticosteroids, hyaluronic acid, and platelet-rich plasma (PRP). Joint injections are crucial in managing joint pain, reducing inflammation, and improving the quality of life for individuals suffering from joint conditions. c, providing valuable information on the different types of joint injections, common conditions that may require them, the procedure itself, post-injection care, risks and complications, and the importance of follow-up and long-term management.
Joint injections offer several benefits in managing joint pain and inflammation. Firstly, they can provide targeted pain relief directly to the affected joint, which can be especially beneficial when other conservative treatments, such as oral medications or physical therapy, may not provide adequate relief. Joint injections can help reduce inflammation, swelling, and stiffness in the joint, allowing for improved joint function and mobility. Sometimes, they can also help delay the need for more invasive interventions, such as joint surgery. Joint injections are typically performed as an outpatient procedure and are generally safe and well-tolerated when performed by a qualified healthcare professional. They can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from joint conditions, allowing them to engage in daily activities with reduced pain and discomfort.
Different Types of Joint Injections:
Several types of joint injections may be used depending on the specific condition and needs of the patient. Some of the commonly used types of joint injections include:
- Corticosteroid Injections: Corticosteroids are potent anti-inflammatory medications that can be injected into the joint to reduce inflammation and relieve pain. These injections are commonly used in osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, bursitis, and tendinitis. Corticosteroid injections are known for their immediate pain-relief effects and are typically administered with a local anesthetic.
- Hyaluronic Acid Injections: Hyaluronic acid is a natural component of joint fluid that acts as a lubricant and shock absorber. Hyaluronic acid injections supplement the joint’s natural lubrication in conditions such as osteoarthritis. Hyaluronic acid injections are typically given over several weeks and are known to improve joint function and reduce pain in some patients.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (P.R.P.) Injections: P.R.P. injections involve using the patient’s blood, which is processed to concentrate the platelets, rich in growth factors, and then injected into the joint. P.R.P. injections promote tissue healing and reduce inflammation, making them a potential option for osteoarthritis and tendinitis. P.R.P. injections are a relatively newer and evolving treatment option for joint conditions.
Common Conditions Requiring Joint Injections:
Joint injections are commonly used in the management of various joint conditions. Here are some examples of common joint conditions that may benefit from joint injections:
- Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint condition that occurs when the cartilage that buffers the joints wears down, leading to pain, stiffness and reduced joint function. Joint injections, such as corticosteroid injections or hyaluronic acid injections, can help reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and improve joint function in individuals with osteoarthritis.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is a condition that causes joint inflammation, leading to pain, swelling, and deformity. Joint injections, including corticosteroid injections or other disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (D.M.A.R.D.s), can help reduce inflammation and manage the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, improving joint function and quality of life.
- Bursitis is the tenderness of tiny fluid-filled sacs called bursae that cushion the joints. Bursitis can cause pain, swelling, and limited joint mobility. Joint injections with corticosteroids or local anesthetics can help reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and improve joint function in individuals with bursitis.
- Tendinitis is the inflammation of tendons, the thick cords that connect muscles to bones. Tendinitis can cause pain, swelling, and limited joint movement. Joint injections with corticosteroids or other anti-inflammatory medications can help reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and promote healing in individuals with tendinitis.
- Gout is arthritis due to uric acid crystals in the joints, leading to severe pain, swelling, and redness. Joint injections, such as corticosteroids or medications to lower uric acid levels, can help reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and manage gout symptoms.
The Joint Injection Procedure:
Joint injections are typically performed by qualified healthcare professionals, such as rheumatologists, orthopedic specialists, or pain management physicians. It is usually done in an outpatient room and involves the following step-by-step process:
- Local Anesthesia: Before the joint injection, the skin over the injection site is disinfected with an antiseptic solution to minimize the risk of infection.
- Sterilization: Maintaining a sterile environment during the joint injection procedure is essential to prevent infection. The healthcare professional performing the injection will use sterile gloves, a sterile needle, and a sterile syringe to ensure proper sterilization.
- Needle Placement: Once the area is numbed, the medical expert injects the medication into the affected joint with a thin needle. The needle is carefully guided into the joint space using imaging guidance, such as ultrasound or fluoroscopy, to ensure accurate needle placement and medication delivery.
- Medication Injection: The appropriate medication, such as PRP., is injected into the joint. The dosage and type of therapy used may vary depending on the specific condition being treated and the healthcare professional’s judgment.
- Post-Injection Care: After the joint injection, the healthcare professional may apply a sterile bandage to the injection site and provide instructions on post-injection care, which may include avoiding strenuous activities for a certain period, applying ice or heat to the injection site, and monitoring for any signs of infection or adverse reactions.
Potential Risks and Complications of Joint Injections:
As with any medical procedure, joint injections carry some potential risks and complications, although they are generally considered safe. These may include:
- Infection: There is a chance of infection at the injection site, although proper sterilization techniques minimize it.
- Bleeding: There may be a small risk of bleeding at the injection site, especially in individuals taking blood-thinning medications.
- Allergic reactions: Some patients may experience an allergic reaction to the medications used in joint injections.
- Damage to surrounding structures: There is a small risk of inadvertently damaging nearby nerves, blood vessels, or other structures during the needle placement.
- Temporary increase in pain: Some individuals may experience temporary increased pain or discomfort at the injection site after the procedure, which usually resolves independently.
Tips to Minimize Discomfort During the Injection:
- Communicate openly with your healthcare professional about any concerns or fears you may have before the procedure.
- Follow any pre-injection instructions your healthcare professional provides, such as fast if required.
- Practice deep breathing to help you stay calm during the procedure.
- Request local anesthesia to numb the injection site and minimize discomfort.
- Avoid looking at the needle, and stay relaxed during the injection.
- Remember to inform your healthcare professional if you experience unusual or severe discomfort during the procedure.
- Follow all your healthcare professional’s post-injection care instructions to promote healing and minimize potential complications.
Post-Injection Care:
After receiving a joint injection, it is essential to follow proper post-injection care to promote healing and minimize potential complications. Here are some key points to consider:
- Common Side Effects: It is common to experience some side effects after a joint injection, including mild pain or discomfort at the injection site, temporary swelling, bruising, or redness.
- When to Seek Medical Attention: While joint injections are generally safe, it is essential to be aware of any signs of potential complications and seek medical attention if necessary. Signs that may warrant medical attention include severe pain or swelling at the injection site, increased warmth or redness, signs of infection (such as fever or pus), or an allergic reaction (such as difficulty breathing or hives).
- Post-Injection Care Guidelines: Your healthcare professional may provide specific guidelines for post-injection care, including rest, ice, compression, and elevation (R.I.C.E.).
- Restrictions or Limitations in Activities: This may include avoiding certain activities, such as heavy lifting, vigorous exercise, or repetitive motions that may strain the injected joint. It is important to follow these instructions to ensure optimal healing and prevent potential complications.
- Medication and Follow-up: Your healthcare professional may prescribe additional medications, such as pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs, to manage discomfort or swelling after the joint injection.
Follow-up and Long-term Management:
After a joint injection, follow-up appointments and long-term management are crucial for effectively managing joint conditions. Here are some key points to consider:
- Follow-up appointments with your healthcare professional are essential to monitor your progress and determine the effectiveness of the joint injection. Your healthcare professional may evaluate your joint function and assess the reduction of pain and inflammation. These appointments also allow you to discuss concerns or questions regarding your joint condition or the joint injection.
- Joint injections are often part of a larger treatment plan for managing joint conditions. They may be combined with other treatments, such as medication, physical therapy, or lifestyle modifications, to provide comprehensive care. Your healthcare professional may tailor a treatment plan based on your joint condition’s severity and underlying cause, considering your specific needs and goals.
- Joint injections may provide short-term relief, but long-term management is essential for ongoing joint health. To support joint health, your healthcare professional may recommend lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, and a balanced diet. Physical therapy may also be recommended to improve joint strength, flexibility, and function. Ongoing monitoring, such as regular check-ups and imaging studies, may be necessary to assess the progress of your joint condition and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
- Effective management of joint conditions often requires a collaborative effort between you and your healthcare team. This may include your primary care physician, rheumatologist, orthopedic specialist, physical therapist, and other healthcare professionals involved in your care. Regular communication and follow-up appointments with your healthcare team can ensure your treatment plan is optimized and adjusted to achieve the best possible outcomes.
- Educating yourself about your joint condition, treatment options, and long-term management strategies is essential for successful joint care. Understanding the importance of joint injections as part of your treatment plan and being proactive in following long-term management strategies can help you manage your joint condition and optimize your joint health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, joint injections are a valuable option for managing joint pain and inflammation. They can provide significant benefits in improving joint function and quality of life. However, working closely with a qualified healthcare professional is vital to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your needs. With the proper care and management, joint injections can effectively manage joint conditions and optimize joint health.
Thrive Wellness offers joint injections like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections. Our experienced healthcare professionals will assess your joint condition and tailor a treatment plan that meets your needs and goals.
Don’t let joint pain hold you back! Take charge of your joint health with Thrive Wellness. Contact us today and start your journey toward a pain-free and active lifestyle.
Call us to learn more about our services and book your appointment. Thrive Wellness – Your partner in joint pain relief!